Actor Shah Rukh and Director Hirani’s Bollywood-drama movie Dunki is a human story of illegal immigrants.
The story is set in 1995 when a group of friends aspires to immigrate to the UK. But their hope is dampened when they fail to qualify for IELTS, the most recognized test for English proficiency.
Later, they take an illegal route called ‘donkey flights’ to immigrate, only to settle in London as janitors, cab drivers, and tailors. Eventually, they find their way back to India after nearly three decades.
But skilled-based immigration makes up for more inspirational stories.
While there are cases of immigrants ending up in low-wage jobs, economic immigration to Canada, Australia, the UK, and the USA remains aspirational for many.
The fact of the matter in Dunki is its attempt to showcase the difference between the rich and the poor, the highly skilled and low-skilled, and their aspiration for a better life abroad.
Here, we shall explore the flourishing opportunities for Indians under skilled-based economic immigration programs in Canada and Australia.
Basics: Types of Immigration
There are several ways to categorize immigration, but two common approaches are based on motivation and immigration status.
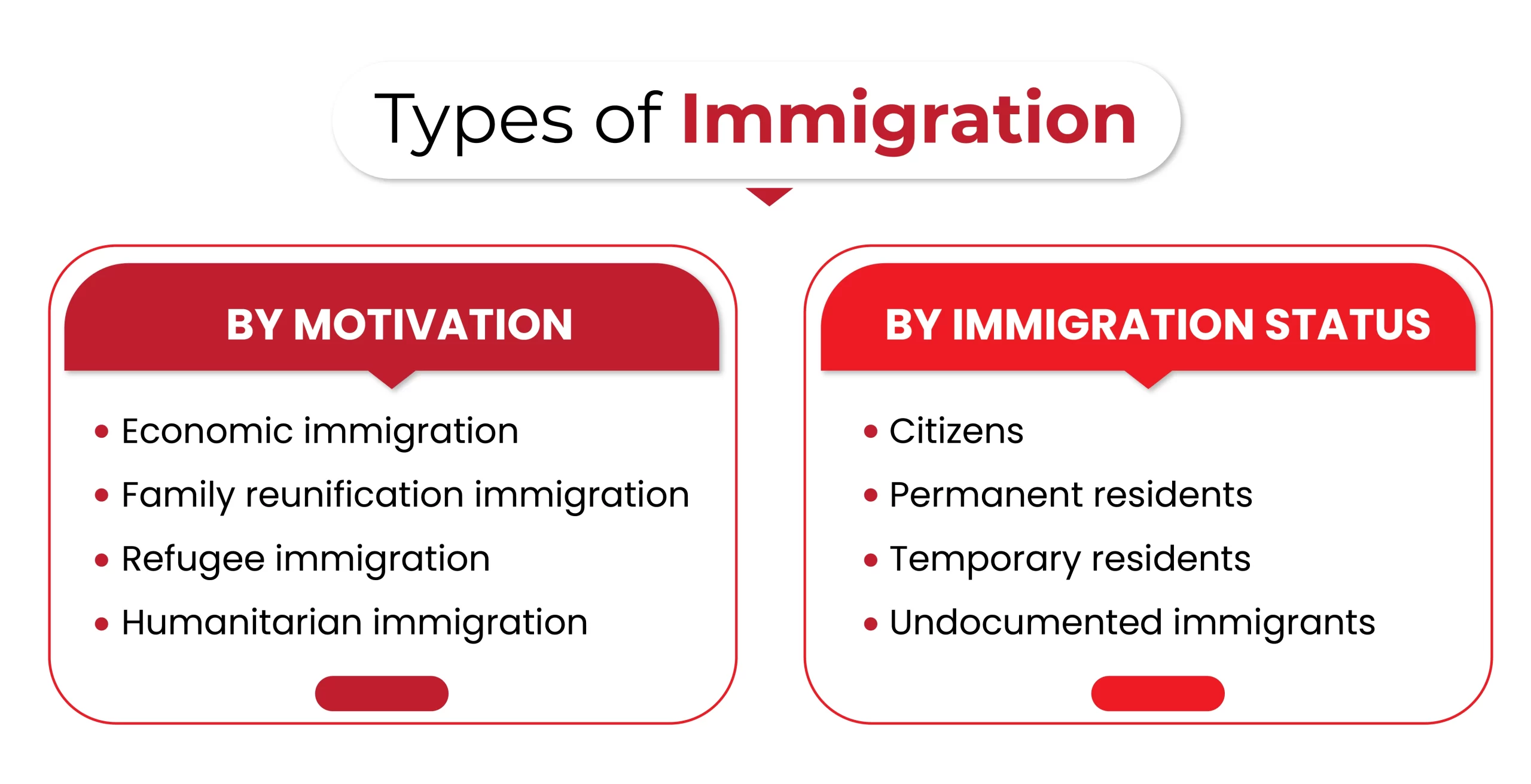
By Motivation:
1. Economic immigration is driven by the desire for better economic opportunities, such as higher wages, more job security, or greater career prospects.
2. Family reunification immigration involves people moving to be with close family members who are already citizens or permanent residents of another country.
3. Refugee immigration involves people fleeing persecution or violence in their home country. They may be granted asylum or refugee status in another country.
4. Humanitarian immigration involves people who are granted entry to another country based on humanitarian grounds, such as if they are suffering from a serious illness or have been the victim of a natural disaster.
By Immigration Status:
1. Citizens: People born in a country or who have gone through the process of naturalization to become citizens have the full rights and privileges of citizenship.
2. Permanent residents: People who are not citizens have been granted the right to live and work in a country indefinitely. They may eventually be eligible to apply for citizenship. Canada is the most preferred destination to obtain PR.
3. Temporary residents: People allowed to live and work in a country for a limited period, typically for reasons such as studying, working, or visiting family.
4. Undocumented immigrants: People who are living in a country without legal authorization. They may be at risk of deportation.
Numbers Check: Indians in Canada & Australia
Both Canada and Australia have witnessed a significant rise in the number of Indian immigrants in recent years, primarily driven by economic factors. Let’s delve into the statistics and trends:
| Feature | Canada | Australia |
| Indian Population | 1.8 million (5% of total) | 800,000 (3.5% of total) |
| Population Growth since 2001 | 200% | 150% |
| Primary Immigration Pathway | Skilled worker programs | Points-based system (skilled & semi-skilled) |
| Economic Contribution | High, key roles in various sectors | Significant, across diverse occupations |
| Regional Distribution | Concentrated in major cities (Toronto, Vancouver) | More spread out across major cities (Sydney, Melbourne) |
Both Canada and Australia have thriving economies with strong demands for skilled labor in various sectors like IT, healthcare, and engineering. These align well with the skillsets of many Indian professionals.
Read more>> Canada’s Green Tech Industry Presents Exciting Employment Opportunities for Immigrants
Further, both countries have consistently ranked high in terms of quality of life, offering factors like stable political systems, excellent education and healthcare systems, and multicultural environments, appealing to families and individuals seeking a better future.
Comparison: Canada vs Australia Immigration Points System
Canada generally has a more points-based system favoring skilled workers, while Australia has a broader system encompassing skilled and semi-skilled occupations. This might make Canada initially more appealing to highly skilled professionals.
The Express Entry system in Canada manages applications for direct PR. It includes candidates qualifying under the Federal Skilled Worker Program, the Federal Skilled Trades Program, and the Canada Experience Class. Furthermore, candidates with prior provincial nominations get additional points to qualify easily for the selection draws.
In recent times, Canada Express Entry has held category-based selection draws. It invites candidates based on their work experience in a particular occupation alone. The selection draws for six categories have been announced so far:
1. Healthcare
2. STEM professions
3, Trades
4. Transport
5. Agriculture and agri-food and
6. French-language proficiency.
Whereas, there are four visa subclasses for skilled immigration in Australia. You can qualify under two direct pathways for Australian PR (Subclass 189, Subclass 190) or two provincial pathways (Subclass 491, Subclass 188).
Let’s compare the core human capital criteria for qualification including Age, Work Experience, Language Proficiency, and Education.
1. Applicant Age Criterion
Canada Immigration Points System |
Australia Immigration Points System |
||
| Age Group | Points | Age Group | Points |
| 18-35 years | 12 | 18-24 years & 33-39 years | 25 |
| 36-40 years | 11-7 | 25-32 years | 30 |
| 41-46 years | 6-1 | 40-44 years | 15 |
| 47 years & above | 0 | 45 years & above | 0 |
In terms of age criteria, Canada awards maximum points to the younger population over 18 years who would typically pursue higher education before gaining work experience in related occupations.
On the other hand, Australia prefers candidates who are in their prime working age (25-32 years) to qualify for permanent residency.
2. Applicant Work Experience Criterion
Canada Immigration Points System |
Australia Immigration Points System |
||
| Work Experience | Points | Work Experience | Points |
| 1 year | 09 | 1-3 years (outside Australia) | 0 |
| 2-3 years | 11 | 3-4 years (outside Australia) | 05 |
| 4-5 years | 13 | 5-7 years (outside Australia) | 10 |
| 6+ years | 15 | 8+ years (outside Australia) | 15 |
Australia is biased in awarding points based on work experience.
Australia awards maximum points to eligible skilled workers who have had work experience inside Australia. For example,
1. 3-4 (experience in Australia): 10 points
2. 5-7 (experience in Australia): 15 points
3. 8+ (experience in Australia): 20 points
On the other hand, Canada remains neutral and prefers any candidates with work experience outside or inside Canada.
Australia considers eligible candidates with more than 3 years of work experience as against Canada which considers skilled workers for immigration with just over 1 year of work experience.
Contact our immigration consultants to know the latest in-demand occupations for immigration.
3. Language Proficiency Criterion
Canada Immigration Points System |
Australia Immigration Points System |
||
| English Proficiency | Points | English Proficiency | Points |
| CLB 9 or higher | 24 | Competent English | 0 |
| CLB 8 | 20 | Proficient English | 10 |
| CLB 7 | 15 | Superior English | 20 |
The distinguishing factor here is Canada has two official languages: English and French, whereas Australia considers English as its official language. Therefore, interested candidates have to qualify for language proficiency according to the requirements of the permanent residency program.
CLB stands for Canadian Language Benchmark (CLB) and is equivalent to the standard proficiency test available for English and French. Those who show proficiency in French are given an additional 4 points along with their band score in CLB.
4. Applicant Education Criterion
Canada Immigration Points System |
Australia Immigration Points System |
||
| Education | Points | Education | Points |
| Degree/Diploma | 19 | Degree/Diploma | 10 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 21 | Bachelor’s Degree | 15 |
| Doctorate | 25 | Doctorate | 20 |
Canada is more liberal in awarding assessment points based on the applicant’s educational qualification. This is more because Canada allows for the direct immigration of eligible candidates even without study or work experience in any of the Canadian provinces or territories.
Further, Canada awards assessment points for additional categories like
1. HS or SC Diploma: 5 points
2. College Certificate: 15 points
3. BS / MBA / Master’s: 23 points
Both countries favor retaining international students after graduation. While Canada awards a Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP) for 3 years, Australia also offers a flexible work visa for graduating students. These visa holders gain work experience inside the country and may be eligible to qualify for permanent residency later.
Some minor details may have been overlooked here for the sake of uniformity. Contact our immigration consultants now for the Canada vs Australia immigration points system based on your profile.
The Verdict
The movie Dunki addresses an important issue of immigration and questions the divide between high-skilled and low-skilled in aspirational Western countries. It brings forward the plight of illegal immigration in a dramatic way.
However, skilled-based economic immigration is still relevant in countries like Canada, the UK, the USA, and Australia. Several individuals have made their fortunes by legally immigrating to such developed countries.
To know more about existing opportunities and eligibility, book a free appointment with expert immigration counselors at CanApprove.
Meanwhile, go watch ‘Dunki’ if you’re a fan!





